The Transformative Power of Visual Intelligence Systems in Modern Diagnostics

Revolutionizing Visual Quality Enhancement
Modern computational systems have reached unprecedented levels in refining visual data quality. These sophisticated algorithms demonstrate exceptional capability in identifying and rectifying imperfections that would challenge even experienced human editors. The efficiency of these systems often produces results that not only match but frequently exceed traditional enhancement techniques, particularly in maintaining fine details while improving overall clarity. What truly sets this technology apart is its contextual awareness - the system evaluates each image as a complete composition rather than isolated elements.
Advanced Pattern Recognition in Visual Data
Contemporary visual analysis platforms can automatically detect and classify objects with precision that rivals human expertise across numerous applications. In healthcare diagnostics, these systems assist professionals in identifying potential health concerns, while in manufacturing they serve as tireless quality control inspectors. This automation allows human experts to dedicate their time to higher-level analysis and decision-making, creating a more efficient division of cognitive labor.
The adaptability of these systems is particularly noteworthy - they can be trained to recognize anything from specialized mechanical components to microscopic cellular structures. This flexibility, combined with their rapid processing speed, represents a significant advancement over traditional manual inspection methods.
Precision Measurement Capabilities
The quantitative analysis features of modern visual processing tools provide measurements with accuracy that transforms data collection processes. These capabilities prove especially transformative in technical and scientific applications where precision is paramount. Agricultural operations, for example, benefit from detailed crop assessments that optimize resource distribution and improve yield predictions. The automation of these measurement processes opens new possibilities for data-driven decision making across multiple sectors.
Contextual Understanding of Visual Information
Beyond simple object identification, these systems offer nuanced interpretation of visual relationships and contexts. This deeper analysis can reveal insights and patterns that might escape human observation, particularly in complex visual environments. Environmental scientists benefit tremendously from this technology's ability to detect subtle ecological changes over time or analyze intricate biological systems.
The integration capabilities of these systems allow for cross-referencing with extensive databases, enabling comprehensive analysis from limited visual data sets. This creates opportunities for more informed conclusions from visual evidence.
Operational Efficiency Advantages
The implementation of automated visual analysis systems frequently yields substantial operational improvements and cost reductions. By automating labor-intensive processes, organizations achieve both time savings and error reduction, leading to improved outcomes whether in medical settings or industrial quality assurance. The resulting improvements in workflow efficiency often translate to measurable economic benefits for implementing organizations.
Democratizing Vision Health Services
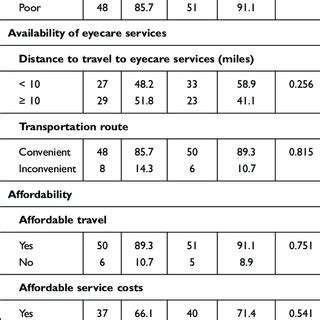
Universal Access Initiatives
Creating inclusive digital environments requires going beyond basic compliance to embed accessibility considerations throughout the design process. Thoughtful implementation of features like auditory navigation aids and adaptive interfaces benefits not only users with specific needs but enhances the experience for all users. True digital inclusion means designing with the full spectrum of human diversity in mind, considering various physical, sensory, and cognitive differences.
The philosophy of inclusive design recognizes that solutions created for specific accessibility challenges often lead to innovations that benefit the broader population. This approach fosters creative problem-solving that expands the potential user base while promoting social equity in technology access.
Economic Accessibility Solutions
Financial barriers remain a significant obstacle to universal technology access. The cost of specialized equipment, software, and connectivity can exclude economically disadvantaged populations from essential services. Effective strategies for reducing these barriers include developing tiered pricing models, establishing community technology centers, and creating public-private partnerships to subsidize access costs.
Eliminating economic obstacles to technology access is fundamental to creating equitable participation in our increasingly digital society. Innovative financing approaches and collaborative programs can help bridge this divide, ensuring that financial limitations don't prevent individuals from accessing vital digital resources.
Comprehensive Inclusion Strategies
Addressing both technological and economic barriers requires coordinated efforts across multiple sectors. Successful initiatives often involve partnerships between educational institutions, community organizations, and policy makers to develop comprehensive solutions. These programs combine access provision with education on effective technology use, creating sustainable pathways to digital inclusion.
Holistic approaches that address both accessibility and affordability create the most effective and lasting solutions. By combining resource provision with education and policy initiatives, we can build a digital landscape that truly serves all members of society.
The ultimate goal is to create technological ecosystems where all individuals can participate fully regardless of physical ability or economic circumstance, leading to more connected and empowered communities.