Decentralized Ledger Technology: Redefining Trust and Transparency
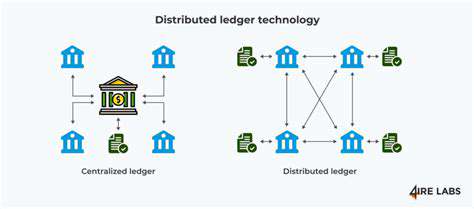
In today's digital landscape, Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is transforming how industries handle data and transactions. Unlike traditional centralized systems, DLT eliminates single points of failure by distributing information across multiple nodes. Originally popularized by cryptocurrencies, this technology now offers groundbreaking solutions for property transactions, ensuring unparalleled security and verifiable records without intermediaries.
Core Features of Modern DLT Systems
What sets contemporary DLT apart is its network architecture. Information isn't stored in one location but duplicated across numerous computers worldwide. This redundancy makes the system virtually tamper-proof and censorship-resistant. Once data enters the ledger, it becomes permanent - creating an auditable trail that builds confidence among all participants. The technology's design inherently prevents unauthorized alterations while maintaining complete transaction histories.
Advanced Protection Mechanisms
Modern decentralized systems employ cutting-edge cryptographic methods to safeguard sensitive information. Through sophisticated encryption and digital signatures, DLT ensures only authorized parties can access or modify data. These security measures have proven particularly valuable in real estate transactions where document authenticity is critical. The technology also allows customizable privacy settings, enabling selective information disclosure when required by law or business needs.
Cross-Industry Implementation
While financial applications initially drove DLT adoption, its uses now span multiple sectors. Property markets benefit tremendously from the ability to track ownership histories and streamline transfers. Other fields like medical records management and logistics also leverage DLT's capacity to maintain immutable audit trails. The technology reduces paperwork, minimizes fraud, and accelerates processes that traditionally required extensive verification.
Current Limitations and Solutions
Like any emerging technology, DLT faces growing pains. Network expansion can strain processing capabilities, and different platforms sometimes struggle to communicate. Developers are actively working on solutions including layer-2 scaling and standardized protocols. Regulatory adaptation presents another challenge, as lawmakers work to balance innovation with consumer protection in this rapidly evolving space.
Emerging Innovations
The next generation of DLT solutions focuses on enhanced performance and accessibility. Breakthroughs in consensus mechanisms and smart contract functionality promise more efficient systems. Integration with artificial intelligence could automate complex processes while maintaining security. These advancements will likely make the technology more practical for everyday business applications and mass adoption.
Understanding Blockchain's Position
Often confused with DLT, blockchain represents just one implementation of the technology. Its block-based structure provides particular advantages for transaction verification and smart contracts. However, alternative DLT models like directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) offer different benefits, demonstrating the technology's versatility beyond its most famous application.
Enhanced Security and Transparency through Immutability

Modern Authentication Methods
Contemporary security systems now incorporate multiple verification layers to protect sensitive property records. Beyond traditional passwords, solutions now combine device recognition, biometric scans, and one-time codes. This multifaceted approach makes unauthorized access exponentially more difficult while maintaining user convenience. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, these advanced protections become essential for safeguarding valuable assets and personal data.
Biometric authentication has emerged as particularly effective, using unique physical characteristics that can't be easily replicated or stolen. The combination of facial recognition and behavioral biometrics provides both security and seamless user experience. These methods significantly reduce fraud risks compared to conventional password systems while speeding up legitimate access.
Next-Generation Data Protection
Encryption technology has advanced dramatically in recent years. Modern systems utilize algorithms that would take centuries to crack with current computing power. This protection extends beyond simple data storage to secure all transaction communications. For property transactions, this means sensitive financial details and personal information remain confidential throughout the entire process.
New cryptographic techniques like post-quantum cryptography are being developed to future-proof systems against emerging threats. These innovations ensure long-term security even as computing capabilities advance. The implementation of such robust encryption standards provides peace of mind for all parties involved in sensitive transactions.
Comprehensive Activity Monitoring
Transparent record-keeping forms the backbone of trustworthy systems. Detailed logs track every access attempt and modification, creating an unforgeable history. This capability proves invaluable for resolving disputes, investigating suspicious activity, and demonstrating regulatory compliance. The ability to verify every action builds confidence among users and regulators alike.
Real-time monitoring systems can now detect and alert administrators to unusual patterns immediately. This proactive approach to security helps prevent breaches before they occur rather than just documenting them afterward. The combination of comprehensive logging and intelligent analysis creates a security environment that's both reactive and predictive.
Precision Access Management
Modern systems implement sophisticated permission structures that go beyond simple user roles. Granular controls can restrict access to specific document fields or functions based on multiple factors including location, device, and time of access. This precision minimizes potential damage from compromised credentials while ensuring authorized users have appropriate access.
The principle of least privilege has become standard practice in security design. By granting only essential permissions, systems dramatically reduce their attack surface. Regular access reviews and automated permission expiration further enhance security by preventing outdated or unnecessary privileges from persisting in the system.