Introduction to Low Latency and 5G
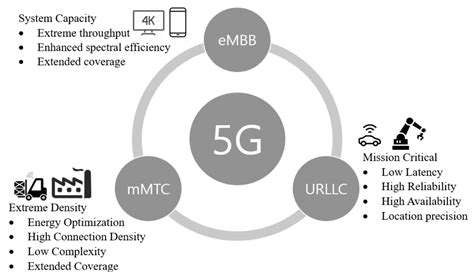
Understanding Low Latency
Low latency represents the brief time gap between initiating an action and receiving a response in technology systems. Typically quantified in milliseconds, this metric is vital across numerous sectors, including interactive entertainment and high-frequency trading. Cutting down latency dramatically elevates user satisfaction and boosts the performance of mission-critical operations. Faster response times lead to fluid interactions and a more polished user journey, especially in scenarios demanding instant feedback.
Imagine a low-latency network as an express courier service - your requests are delivered almost instantly. In contrast, high latency resembles conventional mail delivery, where responses arrive frustratingly late.
The Role of 5G in Reducing Latency
The advent of 5G cellular technology is transforming digital communication through unprecedented latency reductions. With substantially increased bandwidth and lower response times than its predecessors, 5G enables a new generation of real-time applications. Its infrastructure supports massive device connectivity while maintaining lightning-fast data transfer speeds. These capabilities are revolutionizing industries that depend on instantaneous data exchange.
Latency Impact on Various Applications
Minimal latency proves indispensable across multiple domains. Competitive gaming benefits from reduced lag, allowing instantaneous reaction to gameplay events. Financial markets rely on split-second trade executions where milliseconds can determine profit margins. Industrial automation systems demand precise timing for robotic controls, making low latency absolutely essential for operational safety and efficiency.
Latency and Network Architecture
Network design significantly influences latency performance. Physical distance between nodes, traffic congestion levels, and routing efficiency all contribute to total delay. Strategic infrastructure placement and optimized transmission protocols can yield substantial improvements in responsiveness.
Future Trends and Innovations
The technological race for lower latency continues unabated. Edge computing represents a paradigm shift by processing data nearer to its source, dramatically cutting transmission times. Emerging signal processing techniques and next-generation network protocols promise to push latency boundaries even further in coming years.
The Critical Role of Latency in Modern Applications
Understanding Latency in Modern Applications
Contemporary applications define latency as the interval between user input and system response. Even minor delays measured in milliseconds can negatively affect usability. Developers must thoroughly comprehend latency's multifaceted nature when designing responsive systems. Multiple elements contribute to delay, including network performance, server capacity, and software efficiency.
The Impact of Latency on User Experience
Excessive latency creates frustrating user experiences characterized by sluggish performance. Modern users expect near-instantaneous responses; any perceptible delay diminishes perceived quality. Interactive platforms particularly suffer when latency causes synchronization issues between participants.
Latency in Real-Time Applications
Real-time systems have exceptionally stringent latency requirements. Video conferencing platforms, collaborative tools, and live streaming services all demand flawless synchronization. Even minor delays can disrupt communication flow and degrade functionality.
Latency and Network Infrastructure
Network architecture fundamentally determines latency characteristics. Geographical server distribution, connection quality, and traffic management all influence response times. Optimizing these factors remains crucial for delivering smooth digital experiences.
Server-Side Optimization Strategies
Backend optimizations like query refinement, intelligent caching, and efficient algorithms can substantially reduce processing delays. These server-side improvements complement network enhancements for comprehensive latency reduction.
5G and the Promise of Low Latency
5G networks offer revolutionary latency improvements that will transform IoT applications and mobile services. The technology's rapid data transmission enables previously impossible real-time use cases across multiple industries.
Future Trends in Latency Reduction
Emerging technologies like distributed edge computing and quantum networking promise to further minimize latency. These advancements will enable increasingly sophisticated real-time applications with global reach.
Transformative Applications Enabled by 5G Low Latency
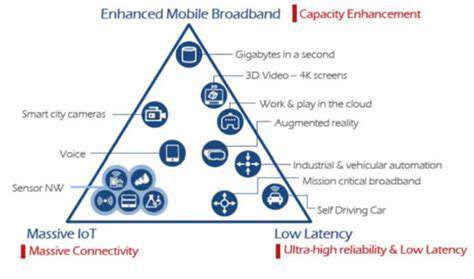
Enhancing User Experiences
Modern applications prioritize intuitive interfaces that blend seamlessly with user workflows. Sophisticated personalization algorithms adapt system behavior to individual preferences, creating uniquely tailored experiences. This adaptive capability represents a quantum leap in user engagement and satisfaction.
Revolutionizing Business Processes
Enterprise applications leverage low-latency connectivity to automate operations and deliver real-time analytics. These systems integrate smoothly with legacy infrastructure while driving operational efficiencies. Seamless integration capabilities prove critical for maximizing ROI on digital transformation initiatives.
Driving Innovation and Growth
Low-latency platforms enable entirely new business models and service offerings. Rapid iteration cycles powered by instant feedback loops accelerate innovation. These capabilities empower organizations to maintain competitive advantage in fast-moving markets.
Improving Accessibility and Inclusivity
Next-generation applications incorporate universal design principles for broader accessibility. Features like voice control and screen reader compatibility ensure equal access for users with diverse needs. This inclusive approach benefits both individuals and the digital ecosystem as a whole.