Predictive Modeling for Outbreak Detection and Response
Predictive Modeling Techniques
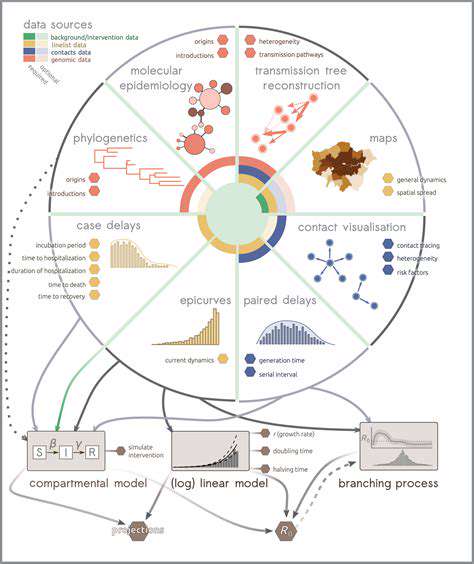
Predictive modeling plays a crucial role in understanding and mitigating the impact of outbreaks. Various statistical and machine learning techniques are employed to forecast the spread of infectious diseases, predict the severity of an outbreak, and identify high-risk populations. These models analyze historical data, including epidemiological trends, environmental factors, and human behavior, to generate predictions about future scenarios.
A key aspect of these models is their ability to identify patterns and relationships within complex datasets. By understanding these patterns, researchers can develop more accurate and reliable predictions, which are essential for informing public health interventions.
Data Sources and Preparation
Accurate predictive models rely on high-quality data. This includes data on confirmed cases, demographics, contact tracing information, and environmental factors. Gathering comprehensive and reliable data is often a significant challenge, particularly during the initial stages of an outbreak when information may be limited or incomplete. Data preprocessing steps, such as cleaning, transforming, and handling missing values, are crucial to ensuring the quality and usability of the data for model development.
Model Selection and Evaluation
Choosing the appropriate predictive model is essential for accurate forecasting. Several models, such as time series analysis, regression models, and machine learning algorithms like neural networks and support vector machines, can be applied depending on the specific characteristics of the outbreak and the available data.
Evaluating the performance of these models is critical. Metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and AUC are used to assess the model's predictive power and to compare different models. This allows for the selection of the most suitable model for the specific outbreak situation.
Outbreak Forecasting and Scenario Planning
Predictive models can be used to forecast the trajectory of an outbreak, helping public health officials to anticipate the potential impact and allocate resources effectively. This forecasting capability is particularly useful for optimizing resource allocation, such as personnel deployment, testing capacity, and the distribution of essential medical supplies.
Scenario planning, based on the predictive models' outputs, can help in developing various response strategies. By examining different potential scenarios, public health officials can prepare for a range of outcomes and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Identifying High-Risk Populations
Predictive models can help identify high-risk populations, enabling targeted interventions to protect vulnerable individuals. By analyzing demographic and health data, models can pinpoint groups most susceptible to infection or severe outcomes, allowing for the prioritization of preventive measures and support.
Integration with Public Health Interventions
The ultimate goal of predictive modeling is to inform and improve public health interventions. Integrating the model's predictions into decision-making processes is crucial for developing effective public health strategies. These strategies can range from public awareness campaigns to targeted contact tracing initiatives and the implementation of isolation protocols.
Ultimately, the successful application of predictive modeling for outbreak response hinges on the ability to integrate the models' output with ongoing public health efforts. This integration is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of interventions and minimizing the impact of the outbreak.
Improving Health Equity through Data Analysis

Addressing Systemic Barriers
Improving health equity requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the systemic barriers that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. These barriers are deeply ingrained in societal structures and policies, and addressing them necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the historical and ongoing factors that contribute to health disparities. Understanding these root causes is crucial to developing effective interventions. Eliminating these barriers is fundamental to creating a healthier society for everyone.
Examples include unequal access to quality healthcare, discriminatory practices within the healthcare system, and limited access to healthy food options and safe environments. Addressing these issues requires not only policy changes but also a shift in societal attitudes and priorities.
Promoting Health Literacy and Education
Health literacy plays a critical role in empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health. When individuals understand their health conditions, treatment options, and preventative measures, they are better equipped to advocate for themselves and improve their overall well-being. This includes providing culturally appropriate and accessible health information in multiple languages and formats. It also encompasses teaching essential health skills, such as managing chronic conditions and navigating the healthcare system.
Education about healthy lifestyles, including nutrition, physical activity, and stress management, is also crucial for promoting health equity. This knowledge can empower individuals to make choices that support their well-being and reduce the risk of developing preventable diseases. By equipping communities with the tools and knowledge to take control of their health, we can foster a healthier and more equitable future.
Enhancing Access to Quality Healthcare
Ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare is paramount in achieving health equity. This involves addressing geographic disparities in healthcare access, ensuring that all communities have access to primary care, specialist services, mental health support, and preventative care. This includes actively working to reduce the financial barriers that prevent individuals from accessing necessary care.
Removing bureaucratic hurdles and ensuring that healthcare providers are culturally competent and sensitive to the needs of diverse populations are also crucial components of this strategy. This encompasses addressing issues of language barriers and ensuring the provision of culturally appropriate care.
Fostering Community Engagement and Collaboration
Community engagement is essential for developing effective and sustainable strategies to improve health equity. Engaging community members in the planning and implementation of health initiatives is critical to ensuring that the solutions are tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the community. This requires listening to and valuing the experiences and perspectives of individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Collaboration among various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, community organizations, policymakers, and community leaders, is essential for achieving the desired outcomes. By working together, we can create a more equitable and healthier future for all. This collaboration fosters trust and creates a sense of shared responsibility for improving health outcomes.
Enhancing Public Health Surveillance and Monitoring
AI-Powered Disease Outbreak Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can analyze vast datasets, including social media posts, patient records, and environmental data, to identify patterns indicative of emerging outbreaks. This proactive approach allows public health officials to swiftly respond to outbreaks, potentially preventing widespread illness and death. Early detection, enabled by AI, is crucial in minimizing the impact of infectious diseases, such as influenza or COVID-19, by facilitating rapid implementation of containment strategies.
By processing information at a scale and speed beyond human capabilities, AI can identify subtle changes in disease prevalence or unusual symptoms clusters. This early warning system empowers public health agencies to initiate preventative measures, such as contact tracing, quarantines, and targeted vaccination campaigns, significantly limiting the spread of contagious diseases.
Predictive Modeling for Resource Allocation
AI-driven predictive models can forecast future health needs, enabling public health agencies to optimize resource allocation. These models analyze historical data, current trends, and demographic information to project the potential burden of diseases and the required healthcare resources, such as hospital beds, medical supplies, and personnel.
Accurate predictions enable proactive resource management, preventing shortages during outbreaks. This foresight is particularly crucial in developing countries or regions with limited healthcare infrastructure, where AI-powered projections can help ensure adequate preparedness and response capabilities.
Improving Public Health Campaigns
AI can personalize public health campaigns to maximize their effectiveness. By analyzing individual characteristics and behaviors, AI algorithms can tailor messages to specific demographics, ensuring the information is relevant and engaging. This targeted approach leads to higher public awareness and participation in preventative measures.
AI can also measure the impact of public health campaigns in real-time. This allows for continuous optimization of strategies based on observed outcomes, ensuring that campaigns are highly effective and efficient. Through data analysis, AI enables adjustments to the campaign's messaging, channels, and timing, maximizing the impact on the target population.
Real-Time Monitoring of Environmental Factors
AI can analyze environmental data, such as air quality, water contamination, and climate patterns, to detect potential health risks. This real-time monitoring enables early identification of environmental factors that could trigger outbreaks of vector-borne diseases or other health problems. Environmental data, coupled with AI analysis, allows public health officials to implement preventive measures, like mosquito control programs or water purification initiatives.
By integrating environmental data into public health surveillance systems, AI allows for a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between environmental factors and human health. This holistic approach empowers agencies to address emerging health threats proactively and effectively.
Enhanced Surveillance of Health Behaviors
AI can analyze large volumes of data from various sources, including social media, wearable devices, and mobile health applications, to identify trends and patterns in health behaviors. This analysis can reveal insights into lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and sleep, that could impact public health outcomes.
AI can also identify individuals at high risk for developing chronic conditions or engaging in unhealthy behaviors. This early identification allows for targeted interventions and preventative measures, ultimately promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing the burden of chronic diseases. Personalized health recommendations, based on AI analysis, can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being.