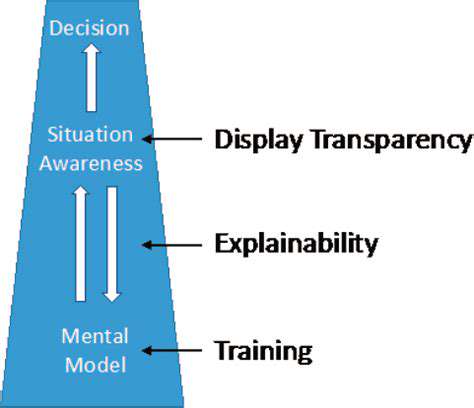
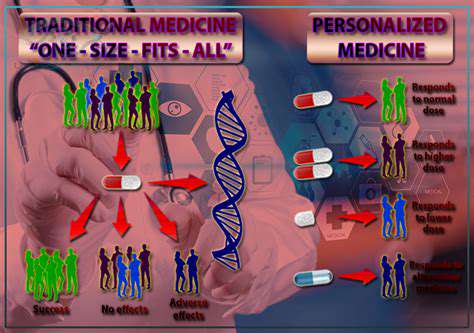
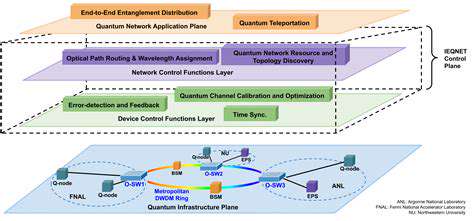
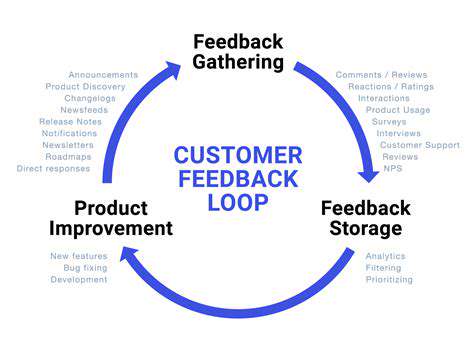
Interactive Visualizations for Enhanced Understanding
Interactive visualizations offer a powerful way to engage with data and concepts in a dynamic and engaging manner. Instead of simply presenting static images, interactive elements allow users to explore different aspects of the information, fostering a deeper understanding and more active learning experience. This dynamic approach transforms passive observation into active exploration, leading to more meaningful insights. Interactive elements like zooming, filtering, and highlighting specific data points enable users to uncover patterns and relationships that might be missed in static representations.
Interactivity Drives Deeper Engagement
Interactive elements, such as clickable charts or interactive maps, enable users to actively participate in their learning experience. This engagement can significantly enhance comprehension and retention. By allowing users to manipulate the data and explore different scenarios, interactive visualizations empower them to construct their own understanding of the presented information. This active participation fosters a stronger connection with the material. This active learning approach is particularly beneficial in educational settings and data analysis contexts.
Improving Data Exploration and Analysis
Interactive visualizations empower users with the ability to explore data in a more in-depth and comprehensive manner. Users can drill down into specific data points, filter information based on their needs, and manipulate variables to observe how changes affect the overall outcome. This level of interaction allows for a more nuanced understanding of the data, leading to more accurate and insightful conclusions. Interactive elements facilitate the identification of hidden trends and patterns that might be overlooked in static representations, significantly improving the quality of data analysis.
Enhancing Accessibility and Usability
Interactive visualizations can be designed to cater to diverse learning styles and preferences. Individuals with different learning styles can engage with the data in ways that best suit their needs. For example, users can adjust the level of detail shown, customize visualizations to focus on specific aspects, and even explore different visual representations, making complex information more accessible. This adaptability fosters a more inclusive learning environment. This interactive approach also makes the information more user-friendly, allowing individuals to navigate and understand the data in a way that is more intuitive and engaging.
Real-World Applications and Benefits
Interactive visualizations have a wide range of applications across various fields. In scientific research, interactive tools can help scientists visualize complex data sets and identify patterns in their findings. In business, interactive dashboards provide real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). Education benefits from interactive visualizations to make complex concepts more digestible and engaging. These dynamic tools can be used to present data in a way that is both informative and entertaining, making learning more effective and enjoyable, ultimately driving better understanding and retention.
Digital Twins and Replication: Protecting Fragile Artifacts

Digital Twin Fundamentals
Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, processes, or systems. They leverage data from various sources, including sensors, operational technology (OT), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to create a dynamic model that mirrors the real-world counterpart. This model allows for simulation, analysis, and optimization of the physical system, providing invaluable insights for improved performance and decision-making.
Crucially, the core function of a digital twin is to act as a dynamic, real-time reflection of the physical system. This is achieved through continuous data updates, enabling the twin to adapt to changes in the physical system and maintain a current, accurate representation.
Replication Strategies
Replication strategies for digital twins vary based on the specific use case and the complexity of the system being modeled. One common approach involves using a combination of data aggregation, model building, and machine learning algorithms to ensure the accuracy and responsiveness of the digital twin. This often involves sophisticated data cleaning and preprocessing methods to ensure the quality and reliability of the data used in the replication process.
Data accuracy is paramount in the replication process. Inaccurate data can lead to inaccurate simulations and flawed insights, significantly impacting the effectiveness of the digital twin. Replication strategies must therefore prioritize data quality to ensure reliable results.
Applications in Various Industries
Digital twins and replication find widespread applications across diverse industries. From manufacturing and energy to healthcare and transportation, the ability to create virtual representations of complex systems allows for predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced safety protocols. For example, in manufacturing, digital twins can simulate various production scenarios, helping to identify bottlenecks and optimize production lines for maximum efficiency.
In healthcare, digital twins can model patient conditions and predict potential health risks, allowing for proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans. The potential applications of digital twins and replication in these diverse industries continue to expand, offering significant opportunities for innovation and improvement.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing digital twins and replication strategies presents certain challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for significant data acquisition and management infrastructure. Ensuring the quality, reliability, and accessibility of the data is crucial for accurate replication and effective analysis. Moreover, integrating various data sources and ensuring data consistency across different systems can be complex and time-consuming.
Another challenge involves the complexity of the algorithms and models required for accurate replication. Developing and maintaining these sophisticated systems demands significant expertise and resources. Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security must also be carefully addressed.
Static, that persistent crackling and hissing sound that seems to invade our audio experiences, is a frustratingly common occurrence. From crackling radios to disruptive phone calls, static interferes with our ability to hear clearly and enjoy the intended audio. This pervasive issue, while often subtle, can significantly detract from the quality of our listening experience and, in some contexts, even cause significant disruption.
Accessibility and Education: Sharing History Globally
Preserving Cultural Heritage Through Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) technology offers a revolutionary approach to preserving cultural heritage, allowing us to engage with history in a dynamic and immersive way. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, AR can bring historical artifacts, architectural wonders, and cultural practices to life, making them accessible to a global audience in a way that traditional methods simply can't replicate. This accessibility is crucial for fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures.
Imagine walking through a historical city and having a detailed explanation of the architecture, the lives of the people who lived there, and the events that shaped the city's history, overlaid onto the buildings in real-time. This is the potential of AR in cultural preservation. It transforms static exhibits into interactive experiences, making the past tangible and relatable.
Bridging the Gap Between Cultures Through AR
AR applications can transcend geographical boundaries, bringing cultural experiences to people regardless of their location. This is particularly important for sharing the stories and traditions of marginalized or underrepresented communities, potentially broadening understanding and empathy. Digital recreations of ancient ceremonies, traditional crafts, or historical events can be shared globally, fostering a sense of interconnectedness and promoting cultural exchange.
Interactive Learning Experiences for Educators
Educational institutions can leverage AR to create engaging and interactive learning experiences. AR apps can provide students with virtual tours of historical sites, allowing them to explore the past in a dynamic and immersive way. This can significantly improve student engagement and comprehension of historical events, fostering a deeper appreciation for diverse cultures and their contributions to human history.
AR can offer a platform for students to analyze historical data, learn about cultural practices, and experience different perspectives in a fun and interactive way. Teachers can use these tools to enhance classroom lessons, making education more engaging and effective.
Accessibility for Individuals with Disabilities
AR technology has the potential to enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities. By providing alternative ways to experience historical sites or cultural events, AR can make these experiences more inclusive and accessible to a wider range of people. For example, visual descriptions of historical events, tactile models of cultural artifacts, and audio guides for historical locations can be incorporated into AR experiences. This is crucial for ensuring that everyone can participate in learning about and appreciating different cultures.
AR's Role in Empowering Local Communities
AR tools can empower local communities by providing them with the means to document and share their own cultural heritage. This is particularly important for preserving the traditions and stories that might otherwise be lost to time. AR can empower local communities to take ownership of their history and share it with the world, fostering a sense of pride and cultural preservation.
This can involve creating AR experiences that highlight local traditions, architectural styles, or historical figures, allowing communities to engage with their heritage in a more personal and meaningful way. This empowers them to become active participants in preserving their culture for future generations.
Addressing Challenges in Implementing AR for Cultural Preservation
While AR offers significant potential for cultural preservation, there are challenges that need to be addressed. The cost of developing and implementing AR technologies can be prohibitive for some institutions or communities. Ensuring the accuracy and authenticity of the historical information presented in AR applications is also crucial. Furthermore, technical limitations and digital divides can create barriers to accessibility for some communities. Overcoming these obstacles is vital to realizing the full potential of AR in cultural preservation.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use of AR
The responsible use of AR in cultural preservation requires careful consideration of ethical implications. Ensuring that cultural representations are accurate, respectful, and avoid perpetuating stereotypes is crucial. Collaboration with local communities and cultural experts is essential to ensure that AR applications reflect diverse perspectives and avoid misinterpretations or inappropriate representations of cultural practices. By addressing these ethical concerns, we can harness the power of AR for positive cultural exchange and preservation.