Blockchain's Role in CBDC Design
Blockchain Technology's Potential
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and secure nature, offers a compelling set of features that could significantly impact the design and implementation of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). Its inherent immutability and transparency could enhance the trust and security of transactions, while its distributed ledger system could potentially reduce reliance on intermediaries and improve transaction speeds. This decentralized approach to record-keeping offers a potentially more robust and resilient system compared to traditional banking infrastructure, making CBDCs more resistant to single points of failure.
The potential for blockchain to streamline cross-border payments and reduce transaction costs is also noteworthy. By eliminating the need for intermediaries in many cases, blockchain-based CBDCs could significantly lower the cost of international transfers, benefiting businesses and individuals alike. This efficiency could be particularly valuable in the global economy, facilitating trade and investment across borders more smoothly.
Security and Privacy Considerations
While blockchain offers strong security features, deploying it within a CBDC framework also presents significant privacy challenges. The transparent nature of blockchain, while contributing to security, can potentially expose sensitive transaction details. Careful consideration must be given to how to balance the need for transparency with the need to protect the privacy of individuals and businesses. Designing appropriate mechanisms for anonymization or pseudonymization is critical for maintaining user trust and complying with privacy regulations.
Scalability and Interoperability Challenges
One of the key hurdles in integrating blockchain into CBDC design is scalability. Traditional blockchain networks can experience bottlenecks when handling a high volume of transactions, and this could hinder the widespread adoption of a CBDC. Finding blockchain architectures and consensus mechanisms capable of handling the massive transaction load anticipated for a CBDC is a crucial consideration. Solutions that incorporate sharding or other scaling techniques would be essential for ensuring the system's overall efficiency and avoiding performance issues.
Interoperability is another critical aspect. A successful CBDC needs to integrate seamlessly with existing financial systems and infrastructure. This includes ensuring compatibility with various payment systems, wallets, and other financial platforms. Lack of interoperability could limit the adoption and usability of a CBDC, potentially hindering its overall effectiveness.
Regulatory and Governance Frameworks
Implementing a CBDC involving blockchain technology necessitates careful consideration of regulatory frameworks. Existing financial regulations may not adequately address the unique characteristics of blockchain-based systems. Clear legal guidelines and governance structures are crucial to define roles, responsibilities, and accountability within the framework. Establishing regulatory oversight mechanisms to address potential risks, such as cyberattacks and fraud, is essential for ensuring the long-term stability and reliability of a blockchain-based CBDC.
Furthermore, jurisdictional issues need to be addressed. A globally adopted CBDC would require international cooperation and agreements to ensure consistent regulations and standards across different countries. This complex regulatory landscape necessitates a thoughtful and collaborative approach to avoid inconsistencies and disputes.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of CBDCs
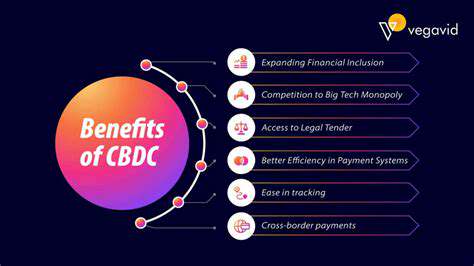
Potential Advantages of New Technologies
The integration of cutting-edge technologies presents a multitude of potential advantages across various sectors. These advancements promise to revolutionize industries, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. From streamlined supply chains to personalized customer experiences, the possibilities are vast and exciting.
Furthermore, these technologies often reduce costs by automating tasks and improving operational efficiency. This can translate to significant savings for businesses and potentially lower prices for consumers. The overall impact on the economy could be substantial.
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
Automation and AI-driven processes can significantly enhance productivity, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks. This shift allows for better allocation of resources and more effective use of time.
Streamlined workflows and improved data analysis are also contributing factors to increased efficiency across diverse industries. This translates to a faster turnaround time for projects and a more responsive approach to customer needs.
Improved Customer Experience
New technologies enable businesses to gather and analyze vast amounts of customer data, leading to a more personalized and tailored experience for each individual. This can result in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. Personalized recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns are two prime examples of how this can improve customer experience.
Cost Reduction and Increased Profitability
Automation and optimized processes can lead to substantial cost reductions for businesses. By minimizing human error and increasing operational efficiency, companies can achieve significant savings that can be reinvested to further growth or passed on to consumers.
Potential for Job Displacement
Despite the many advantages, the adoption of new technologies can also lead to job displacement in certain sectors. Careful planning and retraining programs are crucial to mitigate potential negative impacts on workers.
Ethical Considerations
The rapid advancement of technology raises important ethical questions regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse. Establishing clear ethical guidelines and regulations is essential to ensure responsible development and implementation of these advancements. These concerns require careful consideration and proactive measures to ensure that the benefits are realized while minimizing potential harms.
Security Concerns
With the increasing reliance on technology, data security and cybersecurity become paramount concerns. Stronger security measures and robust data protection protocols are essential to safeguard sensitive information from potential breaches and cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of sensitive data is crucial in the digital age. This requires a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
Technological Considerations in CBDC Development

Hardware Considerations
Choosing the right hardware is crucial for a successful CB implementation. A robust and reliable system is essential to ensure data integrity and prevent disruptions. This involves selecting components that can handle the anticipated data volume and processing demands. Consider factors such as storage capacity, processing speed, and network bandwidth to avoid bottlenecks and ensure smooth operation. Hardware selection should also take into account future scalability needs to accommodate potential growth in data volume or user base.
Furthermore, the physical security of the hardware infrastructure is paramount. Protecting equipment from unauthorized access, theft, and environmental damage is critical to maintain data confidentiality and system availability. Implementing appropriate security measures, such as physical access controls and environmental monitoring, is essential for a secure and reliable CB system.
Software Considerations
Selecting appropriate software is equally important for a successful CB deployment. The software should be compatible with the chosen hardware and seamlessly integrate with existing systems. This ensures smooth data flow and avoids compatibility issues. Consider the software's ability to handle various data formats and ensure the system can adapt to evolving needs and technical advancements.
Software security is also critical. Implementing robust security protocols and regularly updating software to patch vulnerabilities are necessary to protect the system from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Regular security audits and penetration testing are recommended to identify and address potential weaknesses in the system.
Data Management Considerations
Effective data management is essential for the success of any CB system. The ability to store, retrieve, and analyze data efficiently is crucial for drawing actionable insights and making informed decisions. This includes implementing appropriate data storage solutions and developing robust data retrieval mechanisms. data integrity and accuracy are essential to ensure reliable results and avoid errors in analysis.
Furthermore, data security and privacy considerations are paramount. Implementing appropriate access controls and data encryption protocols are essential to protect sensitive information. Adherence to relevant data privacy regulations is crucial to maintain trust and avoid legal issues.
Network Infrastructure Considerations
A reliable network infrastructure is essential for the smooth operation of a CB system. The network must be able to handle the volume of data transmitted between different components of the system and ensure high availability. The network should be designed with redundancy in mind to minimize disruptions caused by network failures.
Network security is equally important. Implementing appropriate security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, is essential to protect the network from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Regular network maintenance and monitoring are crucial to identify and resolve potential issues promptly.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in any CB system. Robust security measures are needed to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Implementing strong authentication protocols, access controls, and encryption mechanisms is crucial to ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities. Staying informed about emerging threats and implementing appropriate security updates and patches are crucial to maintain a secure system.
Scalability and Maintenance Considerations
A CB system should be designed with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth in data volume, user base, and functionality. This means anticipating potential increases in the system's workload and implementing solutions that can handle the added strain. A well-designed system will allow for easy upgrades and modifications as needed, minimizing disruption and downtime.
Implementing a robust maintenance plan is crucial for the long-term success of a CB system. Regular system checks, updates, and backups are essential to ensure system reliability and prevent data loss. Proactive maintenance can minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation.