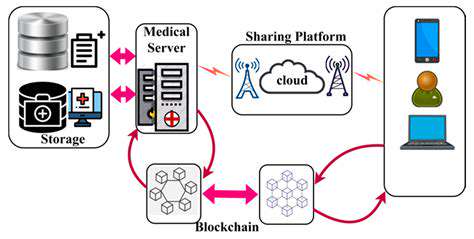
Decentralized Trust and Transparency
Blockchain's inherent decentralized nature fosters a significant advantage in establishing trust and transparency across various processes. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, it reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation. Transactions are recorded on a shared, immutable ledger, visible to all participants, making it exceptionally difficult to alter or hide information. This transparency is crucial for building trust in applications ranging from supply chain management to financial transactions.
Enhanced Security and Immutability
The cryptographic hashing algorithms underpinning blockchain technology create an immutable record of transactions. This inherent security feature makes it exceptionally resistant to tampering and unauthorized modifications. Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity and reliability. This immutability is a key factor in building trust and confidence in systems that require high levels of security.
This also greatly reduces the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks compared to traditional systems, where data can be compromised or manipulated. This enhanced security is crucial for applications where data integrity and reliability are paramount.
Improved Efficiency and Speed
Blockchain's distributed ledger technology enables faster transaction processing times compared to traditional systems that rely on intermediaries. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain can streamline processes, reducing delays and costs. This is especially important in industries where rapid transactions are critical, such as finance and supply chain management. The speed of transactions is a significant advantage in modern business operations, as it reduces bottlenecks and optimizes workflows.
Reduced Costs and Operational Expenses
Blockchain's ability to automate processes and eliminate intermediaries can significantly reduce operational costs. By automating transactions and streamlining workflows, blockchain eliminates the need for manual intervention and reduces the risk of human error. This translates into substantial cost savings for businesses across various sectors. Automation of tasks, like record-keeping and verification, also reduces the need for extensive administrative support, further reducing overall expenses.
Streamlined Cross-Border Transactions
One of the most promising applications of blockchain lies in facilitating cross-border transactions. By providing a secure and transparent platform for these transactions, blockchain can reduce the complexities and costs associated with international payments. The elimination of intermediaries, like banks, can significantly reduce transaction fees and processing times, making cross-border trade more efficient and cost-effective. This is particularly beneficial for businesses operating in multiple countries.
Scalability and Future Applications
Despite its current limitations, blockchain technology has the potential to scale to accommodate a growing number of transactions and users. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving scalability and addressing challenges related to transaction throughput. Future applications of blockchain technology are vast, encompassing various sectors such as healthcare, voting systems, and intellectual property rights management. Continued innovation in this field promises even greater advancements in streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency in the years to come.
Decentralization and Transparency: Key Advantages of Blockchain
Decentralized Control
Blockchain's decentralized architecture removes the reliance on a central authority, like a bank or government. This means that no single entity controls the data or the network, making it more resilient to censorship, fraud, and single points of failure. This distributed control fosters a more secure and trustworthy environment for various transactions and interactions, promoting greater autonomy and reducing the risk of manipulation by a single entity.
Enhanced Transparency
Every transaction on a blockchain is recorded and publicly viewable (depending on the specific blockchain's configuration). This transparency fosters trust and accountability by allowing all participants to verify the validity and history of every transaction. This public record, while not always fully accessible to everyone, acts as a permanent audit trail, which is crucial for building confidence and reducing the potential for illicit activities.
Improved Security
The cryptographic nature of blockchain significantly enhances security. Cryptographic hashing, digital signatures, and other security protocols make it extremely difficult to alter or tamper with data once it's recorded on the blockchain. This immutability of the data ensures integrity and reduces the risk of fraudulent activities, making it a robust solution for various applications requiring high-level security.
Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can streamline processes and reduce transaction costs. Direct peer-to-peer interactions, facilitated by the blockchain, can minimize fees associated with traditional financial systems, leading to cost savings for users. This efficiency translates into faster transaction times, improved operational efficiency, and reduced overhead costs for businesses.
Increased Trust and Accountability
The inherent transparency and immutability of blockchain records create a trustworthy environment for various parties involved. This enhanced trust fosters greater confidence in transactions and interactions. The permanent record of all transactions increases accountability, as every action is traceable and verifiable.
Scalability and Flexibility
Blockchain technology possesses the potential to scale to accommodate a large volume of transactions, making it suitable for various applications, including cross-border payments, supply chain management, and digital identity systems. Its modular design and adaptability make it a flexible solution that can be customized to meet the specific needs of various industries and applications, allowing for ongoing growth and evolution.
Cross-Border Transactions and Global Reach
The decentralized nature of blockchain facilitates cross-border transactions without the need for intermediaries, such as banks. This eliminates the complexities and delays often associated with traditional cross-border payment systems. The global reach of blockchain networks allows for seamless transactions between parties located in different countries, irrespective of their geographical location or financial institutions.