Industrial Automation and Manufacturing

Industrial Automation: A Revolution in Manufacturing
Industrial automation is transforming the manufacturing landscape, driving efficiency, productivity, and precision in production processes. This technological advancement is fundamentally altering how goods are created, from raw materials to finished products. Automation systems are increasingly sophisticated, incorporating advanced robotics, sensors, and data analytics to optimize operations.
The integration of automation in manufacturing has led to significant improvements in output quality and consistency. Automated systems can operate continuously, without the fatigue or errors that can affect human workers, leading to reduced production costs and increased overall profitability.
Key Components of Automated Manufacturing Systems
Automated manufacturing systems rely on several key components, including robotic arms, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and sophisticated software applications. These components work together to execute complex tasks, from material handling and assembly to quality control and inspection.
Robotic systems are central to many automated processes, performing tasks that are repetitive, hazardous, or require high precision. They can be programmed to perform a wide range of operations, from welding and painting to packaging and palletizing.
Benefits of Automation in Manufacturing
The benefits of automation in manufacturing are multifaceted and significant. These advantages extend beyond increased productivity and efficiency to include improved safety, reduced human error, and enhanced product quality.
Improved safety is a critical aspect of automation, as it reduces the risk of injury to workers in hazardous environments. Automation also leads to a significant reduction in human error, ensuring consistent product quality across large production runs.
Challenges in Implementing Automation
Despite the numerous advantages, implementing automation in manufacturing presents certain challenges. One key challenge is the significant upfront investment required for the purchase and installation of automated equipment.
Furthermore, ensuring seamless integration of new automated systems with existing production lines can be complex and require substantial time and resources. This transition period can pose challenges to workforce training and adaptation, often necessitating retraining programs.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation
The future of industrial automation is bright, with continued advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) driving further innovation. These technologies are poised to revolutionize manufacturing processes, leading to even more sophisticated and intelligent systems.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) will further connect and optimize automated systems, allowing for real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, which will significantly improve overall operational efficiency.
The Impact on the Workforce
The implementation of automation raises concerns about its impact on the workforce. While some jobs may be displaced, new roles will emerge that require specialized skills in operating, maintaining, and programming automated systems.
Adapting to these changes will require workforce training and development initiatives to ensure that workers possess the necessary skills for the future of manufacturing. This transition may require significant investments in education and reskilling programs.
Yin and Yang are fundamental concepts in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). They represent opposing yet interconnected forces that exist in everything around us, including our bodies. Yin is often associated with the feminine, passive, and receptive aspects, while Yang embodies the masculine, active, and expressive forces. These forces are not seen as mutually exclusive but rather as complementary aspects of the same whole, constantly interacting and influencing each other. Maintaining a balance between Yin and Yang is crucial for overall health and well-being within TCM.
Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote Patient Monitoring: A Revolution in Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is transforming healthcare by enabling continuous health data collection and analysis outside of traditional clinical settings. This technology allows for proactive intervention, early disease detection, and improved patient outcomes. Through wearable sensors, remote monitoring devices, and telehealth platforms, patients can share vital signs, medication adherence data, and other relevant health information with their healthcare providers. This constant stream of data allows for personalized care plans and timely interventions, ultimately improving the overall quality of life for patients.
The ability to monitor patients remotely, particularly those with chronic conditions, significantly reduces the need for frequent in-person visits. This translates to substantial cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems, freeing up resources for more complex cases and specialized care.
Improving Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart failure, and asthma, require ongoing management and monitoring. Remote patient monitoring plays a crucial role in enabling proactive interventions and personalized care plans. By continuously tracking vital signs and medication adherence, healthcare providers can identify potential complications early on and adjust treatment plans accordingly, leading to better disease management and improved patient outcomes. This proactive approach to care significantly reduces the risk of hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Adherence
Remote patient monitoring empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey. By providing patients with access to their own health data and interactive tools, RPM fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. This increased engagement often leads to improved medication adherence and better self-management skills. Patients become more involved in their treatment, understanding their condition and the importance of following prescribed regimens.
The personalized insights and support provided by RPM tools can also help patients stay motivated and committed to their health goals, ultimately leading to better long-term outcomes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency in Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring offers significant cost-effectiveness advantages to healthcare systems. By reducing the need for frequent in-person visits, RPM lowers healthcare costs associated with transportation, facility utilization, and staff time. This efficiency translates into more resources available for other critical healthcare needs, such as research and development, and specialized care. The long-term cost savings are substantial, as preventative care and early intervention reduce the need for expensive treatments and hospitalizations.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
The increasing use of RPM raises crucial concerns about data security and patient privacy. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access and breaches. Strong encryption, secure data storage, and strict access controls are vital components of any effective RPM system. Patient privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, need to be strictly adhered to, ensuring that patient data is handled responsibly and ethically.
Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
Effective remote patient monitoring requires seamless integration with existing healthcare systems and electronic health records (EHRs). This integration allows for real-time data exchange between different healthcare providers and stakeholders, ensuring a comprehensive and coordinated approach to patient care. Interoperability between different devices and platforms is critical for smooth data flow and avoids data silos, ensuring that all relevant information is readily available to the healthcare team. This comprehensive approach to data sharing is crucial for optimizing patient care.
Retail and Enhanced Customer Experiences

Retail Strategies for a Modern Customer
Retail environments are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. To succeed in this dynamic landscape, retailers must adopt strategies that prioritize the customer experience. This involves understanding consumer behavior, anticipating their needs, and creating an engaging and personalized shopping journey. Modern consumers demand seamless interactions across multiple touchpoints, from online browsing to in-store experiences. This necessitates a holistic approach that integrates digital and physical channels.
A key element of successful retail strategies is the ability to adapt to evolving trends. This includes staying ahead of technological advancements, understanding the latest consumer preferences, and responding effectively to market shifts. Retailers must be agile and responsive to ensure they can meet the ever-changing needs of their target audience. This requires a willingness to experiment with new technologies, strategies, and approaches.
Enhanced Customer Experience through Personalization
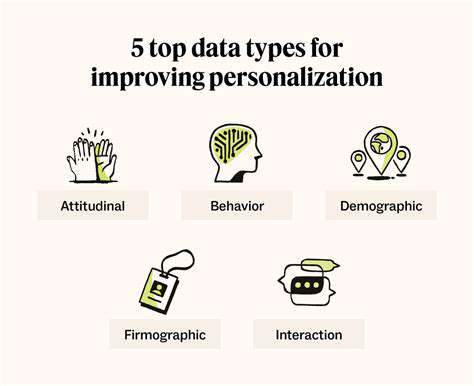
Personalization is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity for retailers aiming to stand out in a crowded marketplace. By leveraging data and technology, retailers can tailor the shopping experience to individual customer needs and preferences. This involves collecting and analyzing customer data to understand their purchasing history, browsing habits, and preferred products. This allows for the creation of targeted marketing campaigns and personalized recommendations, enhancing customer engagement and driving sales.
Creating a personalized experience goes beyond just product recommendations. It also extends to the overall customer journey. Personalized messaging, tailored promotions, and proactive customer service can significantly enhance customer satisfaction. By anticipating customer needs and proactively addressing their concerns, retailers can build stronger, more loyal relationships. This level of personalization fosters a sense of connection and value, making customers feel appreciated and understood.
The Impact of Technology on Retail
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the retail landscape. From online marketplaces and mobile apps to virtual reality and augmented reality experiences, technology is transforming how consumers shop. Retailers must embrace these advancements to provide a superior shopping experience for customers. Integrating technology into all aspects of the business, from inventory management to customer service, can streamline operations and improve efficiency.
The use of data analytics is crucial for understanding customer behavior and preferences. This data-driven approach allows retailers to optimize pricing strategies, personalize marketing campaigns, and predict future trends. Leveraging technology effectively enables retailers to gain valuable insights into consumer needs and preferences, allowing for more informed decision-making. Implementing these technologies requires careful planning and execution to ensure they enhance rather than hinder the customer journey.
The Future of Retail: Omnichannel Integration
The future of retail lies in seamless omnichannel integration. This means creating a unified experience across all channels – online, mobile, and in-store. Customers should be able to seamlessly transition between these channels without experiencing any friction or disruption. This integrated approach fosters a consistent brand experience and allows customers to interact with the brand on their preferred platform.
Omnichannel integration allows for a more holistic view of the customer. By combining data from various channels, retailers can gain a deeper understanding of customer preferences, purchase patterns, and pain points. This comprehensive understanding enables retailers to personalize the customer journey even further, ultimately driving loyalty and repeat business. Providing a consistent experience across all channels strengthens the brand image and fosters customer trust, while also improving operational efficiency.