AI-Powered Solutions for Waste Stream Analysis
Optimizing Waste Collection Routes
AI algorithms can analyze historical waste collection data, including volume, type, and location, to identify patterns and inefficiencies. This analysis can lead to optimized collection routes, reducing travel time and fuel consumption. By strategically adjusting schedules and routes based on real-time data, municipalities can significantly improve the efficiency of their waste management systems, potentially leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Predictive modeling can forecast future waste generation based on historical trends and external factors like weather patterns or events. This foresight allows for proactive adjustments to collection schedules, preventing overflowing bins and ensuring consistent service, which is crucial for maintaining public health and sanitation.
Categorizing Waste for Recycling
AI-powered image recognition and sensor technologies can automatically identify and categorize different types of waste materials. This enables more accurate sorting and processing for recycling purposes. The automated sorting process dramatically improves the efficiency of recycling facilities, allowing them to recover more valuable materials and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Identifying recyclable materials within mixed waste streams can be complex. AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets, can learn to distinguish between various recyclable materials, even when they are mixed or partially obscured, leading to a significant increase in the overall recycling rate.
Predicting Waste Generation Patterns
AI models can analyze various factors, such as population density, seasonality, and event schedules, to predict future waste generation patterns. This advanced forecasting allows for proactive planning and resource allocation, minimizing the risk of overflowing landfills and ensuring efficient waste management practices.
Improving Waste Management Efficiency
Implementing AI-driven solutions in waste management systems can dramatically improve overall efficiency. From optimized collection routes to automated sorting, these solutions streamline processes and reduce operational costs. This efficiency translates to better resource allocation and a more sustainable waste management system, ultimately benefiting the environment and communities.
Reducing Landfill Waste
By identifying and diverting recyclable materials, AI contributes significantly to reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills. This reduction in landfill volume directly impacts environmental sustainability by minimizing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfill operations. The impact on the environment is significant, especially in areas with limited landfill capacity.
Enhancing Public Awareness and Engagement
AI can be used to develop interactive platforms and educational tools to raise public awareness about waste management practices. These platforms can provide personalized information and tips on reducing waste, promoting recycling, and adopting sustainable habits. This proactive approach to raising awareness empowers individuals to contribute to a more sustainable future, emphasizing the importance of responsible waste disposal.
Implementing Smart Waste Bins
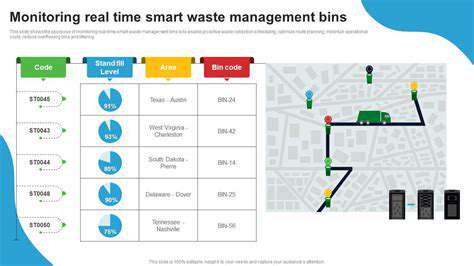
Smart waste bins equipped with sensors can monitor fill levels in real-time, providing valuable data for optimizing collection schedules. This data-driven approach helps waste management teams avoid unnecessary trips to full bins and ensures that collection is performed in the most efficient manner. The use of sensors and data analytics allows for a more responsive and proactive waste management strategy.
Quantum computing, a rapidly emerging field, promises unprecedented computational power, but its potential impact on cryptography is both exciting and deeply concerning. The fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, unlike classical physics, allow for the manipulation of quantum bits (qubits) in ways that unlock the ability to solve problems currently intractable for even the most powerful supercomputers. This inherent power, however, presents a significant challenge to the security of existing cryptographic systems, forcing researchers to develop quantum-resistant alternatives.